XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is the first dedicated scientific satellite from ISRO to carry out research in space-based polarisation measurements of X-ray emission from celestial sources.

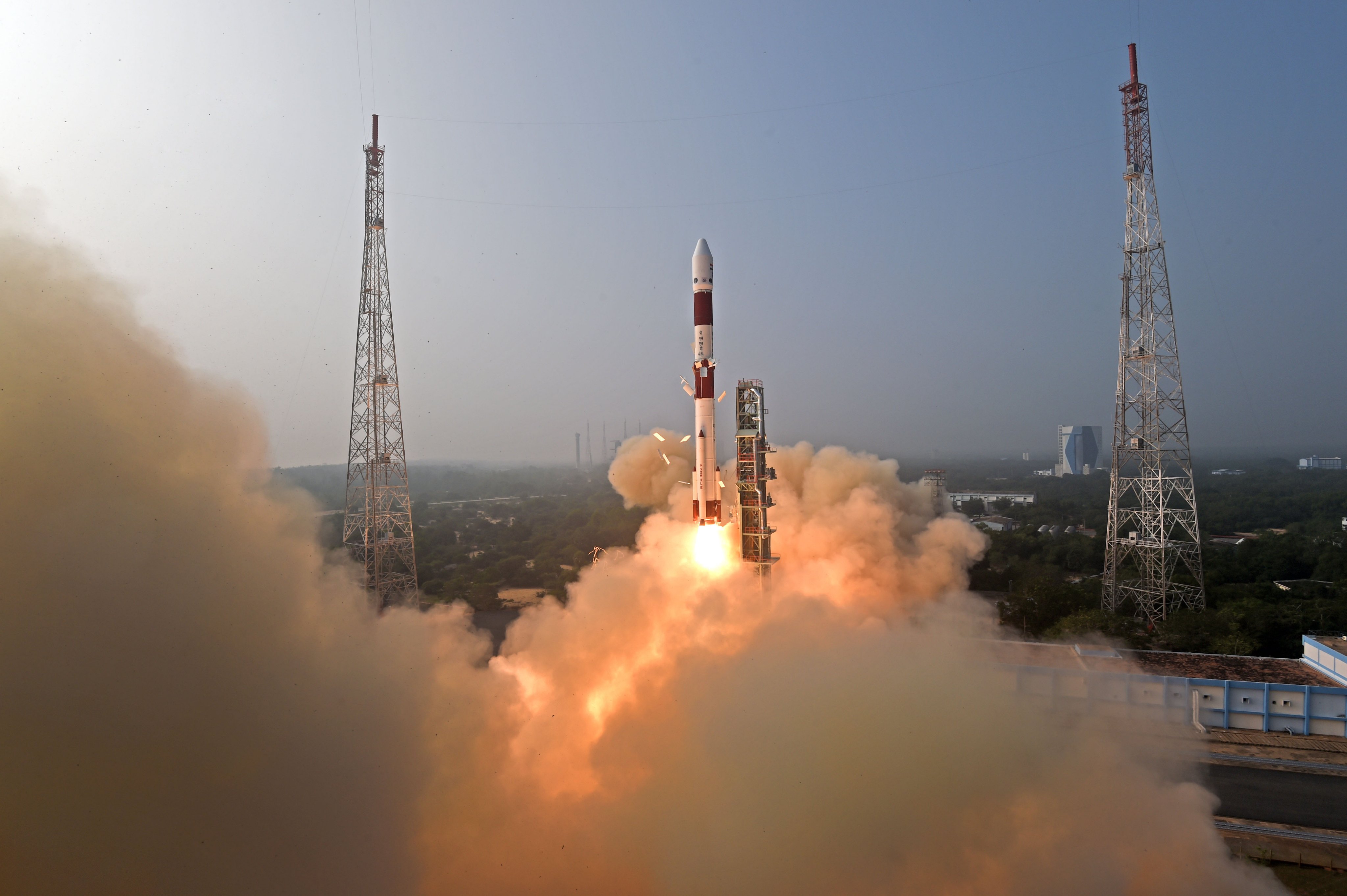
PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission: The Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO) — the national space agency of India, is set to welcome the new year with the launch of its first X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite that will provide insights into celestial objects like black holes, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle rocket on Monday, January 1, 2024. While preparing for any competitive examination, current affairs play an important role. Staying informed about current affairs enhances your general awareness and knowledge about the world, including political, economic, social, and environmental issues. This broader understanding is essential for a career in the civil services.
Speaking of the Main Examination, particularly in the General Studies papers, questions often require candidates to analyze and discuss current events in the context of governance, policy formulation, and societal impact. A strong grasp of current affairs can help you give relevant examples and arguments in your answers. With a three-stage selection process, high competition, and comprehensive knowledge, the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE) is often regarded as one of the most challenging and toughest competitive exams in India.
From objective, and launch date, to PSLV-C58 Vehicle Characteristics; there are key things you must remember during UPSC CSE(Prelims) 2024 preparation. Read below.
PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission: Questions to Keep in Mind While UPSC CSE Prelims 2024 Preparation
What is XPoSat?
XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is the first dedicated scientific satellite from ISRO to carry out research in space-based polarisation measurements of X-ray emission from celestial sources. It carries two payloads namely POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) and XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing). POLIX is realized by Raman Research Institute and XSPECT is by Space Astronomy Group of URSC.
What are the objectives of the PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission?
- To measure polarisation of X-rays in the energy band 8-30keV emanating from about 50 potential cosmic sources through Thomson Scattering by POLIX payload.
- Ÿ To carry out long term spectral and temporal studies of cosmic X-ray sources in the energy band 0.8-15keV by XSPECTpayload.
- Ÿ To carry out polarisation and spectroscopic measurements of X-ray emissions from cosmic sources by POLIX and XSPECTpayloads respectively in the common energy band.

Launch Date
“The launch of the X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is set for January 1, 2024, at 09:10 Hrs. IST from the first launch-pad, SDSC-SHAR, Sriharikota,”ISRO in an official tweet wrote.
🚀 PSLV-C58/ 🛰️ XPoSat Mission:
The launch of the X-Ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is set for January 1, 2024, at 09:10 Hrs. IST from the first launch-pad, SDSC-SHAR, Sriharikota.https://t.co/gWMWX8N6IvThe launch can be viewed LIVE
from 08:40 Hrs. IST on
YouTube:… pic.twitter.com/g4tUArJ0Ea— ISRO (@isro) December 31, 2023
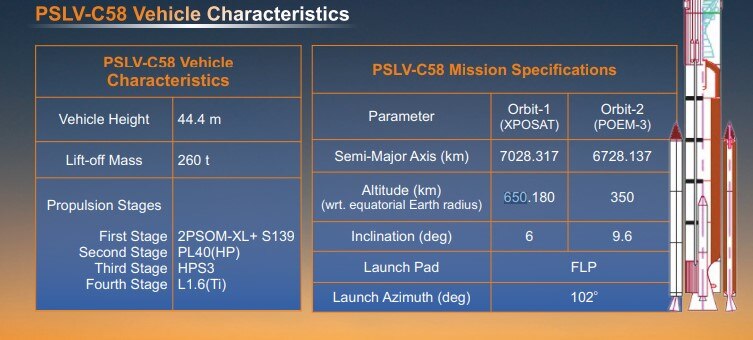
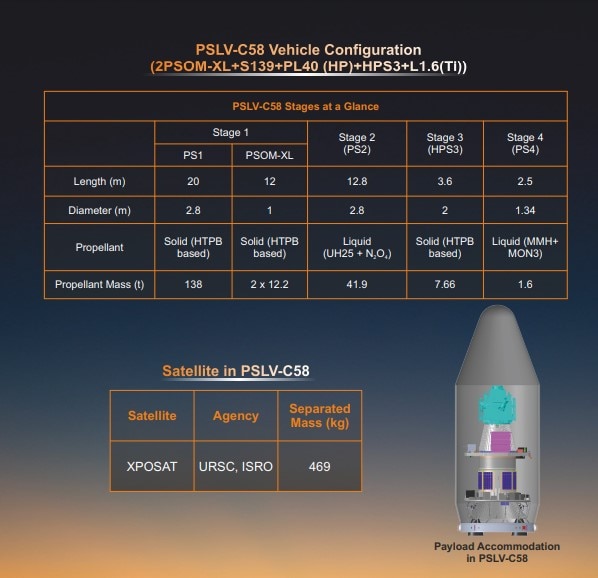
Vehicle Characteristics
As per news agency PTI report, The 44.4-meter-tall PSLV rocket would first deploy the primary satellite into a 650 km Low Earth Orbit around 21 minutes after lift-off and later the scientists would bring the satellite to a lower altitude of about 350 km by restarting the fourth stage of the vehicle, for conducting the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3) experiment.
As per ISRO, The XPOSAT satellite has two payloads:
- POLIX: This will measure the polarimetry parameters (degree and angle of polarization) in medium X-ray energy range of 8-30 keV photons of astronomical origin. The payload is being developed by Ramam Research Institute (RRI), Bangalore in collaboration with U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC). The instrument is made of a collimator, a scatterer and four X-ray proportional counter detectors that surrounds the scatterer. The scatterer is made of low atomic mass material which causes anisotropic Thomson scattering of incoming polarised X-rays. The collimator restricts the field of view to 3 degree x 3 degree so as to have only one bright source in the field of view for most observations. POLIX is expected to observer about 40 bright astronomical sources of different categories during the planned lifetime of XPoSat mission of about 5 years. This is the first payload in the medium X-ray energy band dedicated for polarimetry measurements.
- XSPECT: Will give spectroscopic information in the energy range of 0.8-15 keV. An X-ray SPECtroscopy and Timing payload onboard XPoSat, which can provide fast timing and good spectroscopic resolution in soft X-rays. Taking advantage of the long duration observations required by POLIX to measure X-ray polarization, XSPECT can provide long-term monitoring of spectral state changes in continuum emission, changes in their line flux and profile, simultaneous long term temporal monitoring of soft X-ray emission in the X-ray energy range 0.8-15 keV. An array of Swept Charge Devices (SCDs) provide an effective area >30 cm2 at 6 keV with energy resolution better than 200 eV at 6 keV. Passive collimators are used to reduce the background by narrowing the field of view of XSPECT. XSPECT would observe several types of sources viz X-ray pulsars, blackhole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron star (NS) in LMXBs, AGNs and Magnetars.
PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission Launch Live Streaming: When And Where To Watch
- To watch the live streaming of the PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission launch, students can follow these steps:
- Check ISRO’s Official Website and Social Media:
- Visit the official website of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at www.isro.gov.in for updates and live coverage information.
- Follow ISRO’s official social media accounts on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube for live-streaming links and real-time updates. The Live Streaming for the same can be done via the official website, Facebook, and YouTube page of ISRO.
What are the Scientific Goals of the PSLV-C58/XPoSat Mission?
- To study the distribution of magnetic field, geometric anisotropies, alignment w.r.t line of sight, nature of accelerator in galactic cosmic X-Ray sources by measuring degree of polarization and its angle.
- Ÿ Structure and geometry of magnetic field of neutron stars, mechanism of X-Ray beaming and its relation with luminosity and mass of accretion rate of powered pulsars.
- Ÿ Detailed understanding of galactic black hole binary sources.
- Ÿ To study and confirm about production of X-Rays is either from polar cap of neutron star or outer cap of pulsar magnetosphere.
- Ÿ To distinguish the synchrotron mechanism as dominant over thermal emission in Supernova remnants.
XPoSat satellite Launched successfully.




